About Us
In-depth Analysis of Truck Water Pumps: A Comprehensive Insight from Principles to Maintenance
Views : 5
Update time : 2025-07-17 11:18:46
I. Introduction

As a core component of the engine cooling system, the truck water pump directly affects thermal management efficiency and engine service life. In-depth understanding of its working essence, technical details and full-cycle management is significant for equipment control, cost reduction and industry development.
II. Working Principle of Truck Water Pumps
(I) Power Drive and Energy Conversion
The water pump gets power from the engine via pulleys and couplings, driving the impeller to rotate. The impeller creates a centrifugal force field, moving coolant from the central low-pressure area to the edge high-pressure area, converting mechanical energy into liquid kinetic and pressure energy. Impeller blade design affects coolant flow and pressure, with fluid dynamics optimization reducing losses and improving efficiency.
(II) Dynamic Balance of Coolant Circulation
The water pump drives coolant circulation in closed loops like the engine water jacket and radiator. The thermostat works with it: closing the large cycle for quick warming during cold start; opening it for enhanced 散热 under high loads, maintaining engine thermal balance.
III. Structural Design and Technical Evolution
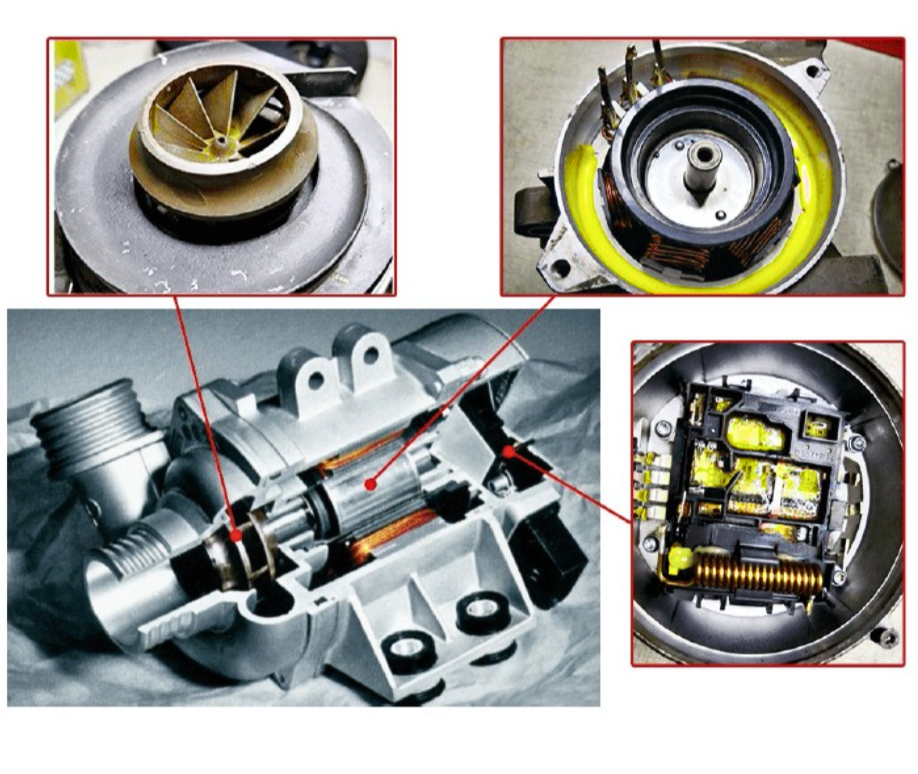
(I) Key Components
- Impeller: New composite impellers (e.g., carbon fiber-reinforced nylon) are lightweight and strong. Fluid simulation-designed blades reduce eddy currents, improving coolant delivery stability for high-speed and large-flow scenarios.
- Shaft Seal: From mechanical seals to dry gas and magnetic seals. Magnetic seals use magnetic fields for torque transmission, with non-contact design reducing leakage risk, suitable for high-end trucks.
(II) Water Pump Types
- Mechanically Driven: Mature, low-cost but limited by engine speed. Optimized belt tensioning mechanisms alleviate speed fluctuation impacts but may have circulation lag in complex conditions.
- Electric: Variable-frequency motor-driven, independent of engine speed, with ECU intelligent control for precise heat dissipation. Used in new energy and high-end trucks but with high integration and electromagnetic compatibility requirements, increasing power consumption and fault points.
IV. Fault Diagnosis and Root Causes
(I) Typical Faults
- Abnormal Noise: Bearing wear (due to poor lubrication or excessive tolerances) causes "buzzing"; impeller loosening (from bolt fracture or fit failure) leads to "clunking", disrupting coolant flow and increasing vibration.
- Water Leakage: Shaft seal leakage relates to coolant impurities and seal wear; pump casing cracks result from thermal fatigue and mechanical impact, reducing system pressure and affecting heat dissipation.
(II) Diagnosis Methods
- Vibration Monitoring: Acceleration sensors collect signals; spectrum analysis identifies bearing fault frequencies and impeller imbalance vibration for early warning.
- Pressure Testing: A test bench measures pressure. Abnormal drops indicate leakage or impeller damage; excessive fluctuations may mean cavitation, requiring checks on liquid level and radiator blockage.
V. Maintenance and Repair Strategies
(I) Preventive Maintenance
- Coolant Management: Select suitable coolants, test regularly. Replace long-life coolants timely to avoid component corrosion.
- Component Life: Use big data to analyze bearing and shaft seal life, establish models based on mileage and conditions, replacing components in advance to prevent faults.
(II) Repair and Renovation
- Fault Repair: Laser welding fixes pump casing cracks; plasma spraying restores worn impellers; strict shaft seal installation controls reduce secondary leakage risk.
- Remanufacturing: Retired pumps are disassembled, cleaned, repaired or with parts replaced, then tested, restoring 80%-90% performance, reducing costs and fitting the circular economy.
VI. Conclusion
Truck water pump technology involves multiple aspects. Mastering it ensures engine reliability, reduces losses and promotes technological progress. With truck intelligence and new energy development, water pumps will become more efficient, intelligent and reliable, requiring continuous industry attention and research.
相关新闻
 Truck Fuel Injectors: The "Precise Valve" for Engine Fuel Supply
Truck Fuel Injectors: The "Precise Valve" for Engine Fuel Supply
Jul 17,2025
This article focuses on truck fuel injectors, introducing their key role as the core component of the fuel supply system, which is to control fuel injection quantity, timing, and atomization effect. It elaborates on their structure, types, analyzes fault manifestations, causes, and diagnostic methods, and provides daily maintenance strategies, helping readers understand their important impact on engine performance.
 In-depth Analysis of Truck Water Pumps: A Comprehensive Insight from Principles to Maintenance
In-depth Analysis of Truck Water Pumps: A Comprehensive Insight from Principles to Maintenance
Jul 17,2025
This article focuses on truck water pumps, exploring their working principles (power drive, energy conversion, coolant circulation balance), structural design, types, fault diagnosis, preventive maintenance and repair, to help master relevant knowledge and support engine operation and industry development.
 Getting to Know Truck Water Pumps: The "Circulation Core" Ensuring Engine Operation
Getting to Know Truck Water Pumps: The "Circulation Core" Ensuring Engine Operation
Jul 17,2025
This article focuses on truck water pumps, introducing their core role as the "heart" of the engine cooling system, which is to drive the circulation of coolant for heat dissipation and maintain the engine at an appropriate operating temperature. It also elaborates on the main structure, common types of water pumps, as well as key points for daily maintenance and fault diagnosis, helping readers gain a preliminary understanding of the importance and related knowledge of truck water pumps.
 Truck Tire Pressure Sensor: A Key Component for Safety and Efficiency
Truck Tire Pressure Sensor: A Key Component for Safety and Efficiency
Jul 15,2025
This article introduces truck tire pressure sensors, expounds their two working principles (direct and indirect types), explains the types and characteristics of built-in and external types, analyzes their significance for truck safety and operational efficiency improvement, mentions mainstream products, performance and selection points, and emphasizes their key role in truck operation.
